
- #PREVIOUS 1 2 3 4 5 HOW TO#
- #PREVIOUS 1 2 3 4 5 CODE#
The item that goes last is the one that comes out first. Stack is an arrangement of items that follows a last-in-first-out order.
#PREVIOUS 1 2 3 4 5 HOW TO#
How to Implement a Stack (LIFO) What is a stack (LIFO)?
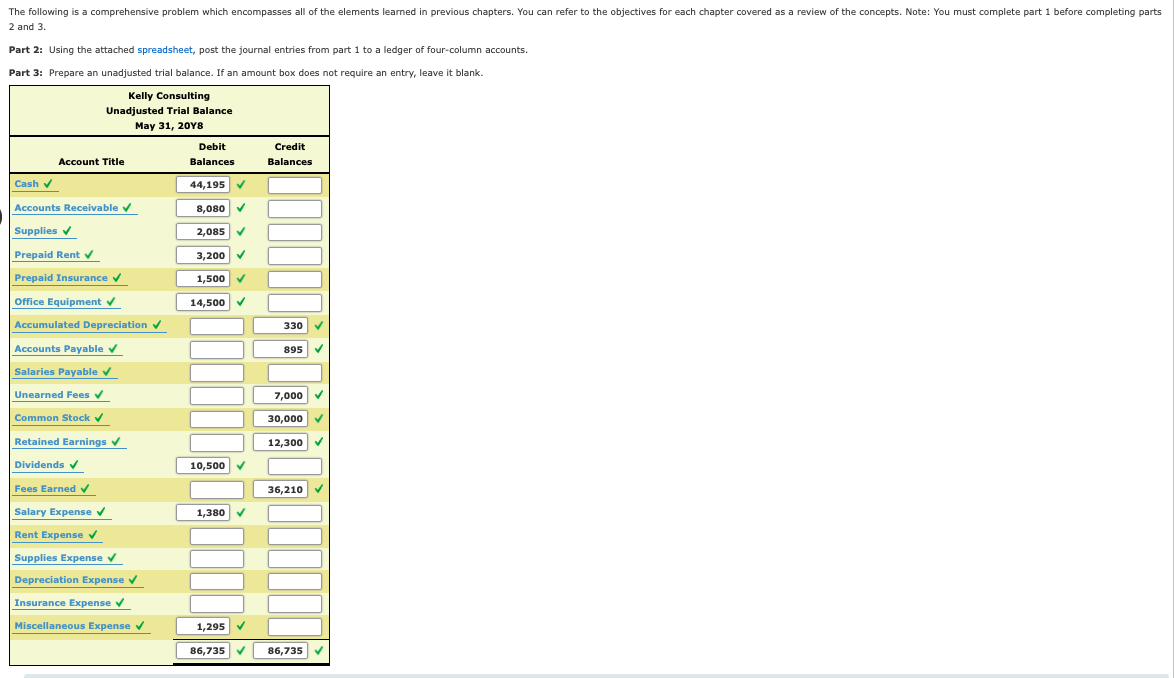
You should use Insert() when insertion is required at a specific index or range of indexes. It is useful when only a single item needs to be inserted.īut if you need to make multiple additions, extend() is a better option as it adds iterable items in one batch. Append() vs Insert() vs Extend()Īppend() always adds a single item at the end of a list. Return is list comprehension.īoth of the methods for filling an empty list are valid and suitable in different scenarios. Notice the commented out lines here: # Return area of square We can modify our previous example to achieve list comprehension.
#PREVIOUS 1 2 3 4 5 CODE#
List comprehension makes the code simple and readable by combining the for loop and append() into a single line. How to populate an empty list using list comprehension We can make the above code efficient by completely skipping the for loop - append() combination and using list comprehension instead. In this example, we are calculating area of a square and appending the result in an array. There are two ways to populate empty lists: using a for loop with append() and using list comprehension. Output: How to populate an empty list using for loop and append() Let's combine two arrays odd and even into a single list using the + operator. Output: Combining arrays using the + operator # starting from last index +1, add items from list B Let's see how we can add lists using slicing.
list implies to start from index 0 until the last item. Missing right index implies until the last index. list means start from index 0 and continue until the end. Missing left index implies starting from index 0. list would return items starting from index 1 up to (not including) index 3. Slicing allows us to select a range of values in a list. Other ways to extend lists in Python: List slicing Print('List after extend():', even_numbers) # add all elements of even_numbers to more_even_numbers The below example combines two lists into a single list. We can add multiple items to a list using the extend() method. How to add multiple items in a list using list.extend() Unable to add multiple items using list.append(). ⚠️Note that trying to append more than one item gives an exception, as list.append() takes only a single argument. We can add a single item at the end of the list using list.append(). Output: How to append an item to a list using list.append() # '21' is inserted at index 3 (4th position) 
Syntax of insert: insert(index, element).Įxample of insert(): # create a list of odd numbers There are more insertion methods and we will look at them later in this post. You can insert items in a list at any index using the insert() method. How to insert items in a list with insert()
 list.extend() – adds iterable items (lists, tuples, strings) to the end of the list. list.append() – always adds items (strings, numbers, lists) at the end of the list. list.insert() – inserts a single element anywhere in the list. We can extend a list using any of the below methods: Print("Length of List: ",len(programming_lang)) Finding the length of a list We can easily find the length of a list using the len() method. Print("At index -5:",programming_lang) Accessing list via negative index. If we wanted to access the last item from the list above, we could also use index -1: programming_lang = You can also access items using a negative index, where -1 represents the last list item. Print("At index 3:",programming_lang) Defining and printing a list Let's write a short program to define a list and access its items: programming_lang = In the image below, "P" is at index "0" whereas "H" is at index "3". This would create a list as shown in the image below: List items against indexes How to access items in a listĪs list items are ordered, you can access them using their index. We can also provide values while creating a list: # Create a filled list We can leave them empty and supply values later in the program: # Create an empty list You create a list using square brackets in Python. Lists are mutable and dynamic which means they can be modified after their creation. Lists have the following properties that make them powerful and flexible: How to implement a stack using list insertion and deletion methods.
list.extend() – adds iterable items (lists, tuples, strings) to the end of the list. list.append() – always adds items (strings, numbers, lists) at the end of the list. list.insert() – inserts a single element anywhere in the list. We can extend a list using any of the below methods: Print("Length of List: ",len(programming_lang)) Finding the length of a list We can easily find the length of a list using the len() method. Print("At index -5:",programming_lang) Accessing list via negative index. If we wanted to access the last item from the list above, we could also use index -1: programming_lang = You can also access items using a negative index, where -1 represents the last list item. Print("At index 3:",programming_lang) Defining and printing a list Let's write a short program to define a list and access its items: programming_lang = In the image below, "P" is at index "0" whereas "H" is at index "3". This would create a list as shown in the image below: List items against indexes How to access items in a listĪs list items are ordered, you can access them using their index. We can also provide values while creating a list: # Create a filled list We can leave them empty and supply values later in the program: # Create an empty list You create a list using square brackets in Python. Lists are mutable and dynamic which means they can be modified after their creation. Lists have the following properties that make them powerful and flexible: How to implement a stack using list insertion and deletion methods. 
Syntax, code examples, and output for each data insertion method.Methods to insert data in a list using: list.append(), list.extend and list.insert().An overview of lists and how they are defined.Lists are a collection of arbitrary objects, just like arrays in other programming languages. Lists are one of the most useful and versatile data types available in Python.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
